Cannabis is known for it’s powerful and intoxicating effects but these effects usually come from THC or delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol which in reality is not present in the raw form of the plant. The natural form has THCa or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid which is the acidic form of THC and it has no psychoactivity at all.
As the plant dries, THCA converts to THC slowly. Heat expedites this conversion in a process known as decarboxylation. Even though THCa is the precursor to psychoactive THC effects, their chemical composition and effects on the body are different. So why does THC give psychoactivity and THCa doesn’t? The reason is because THCa has a three-dimensional shape and it’s larger molecule doesn’t fit into our cannabinoid receptors, specifically the CB1 receptors.
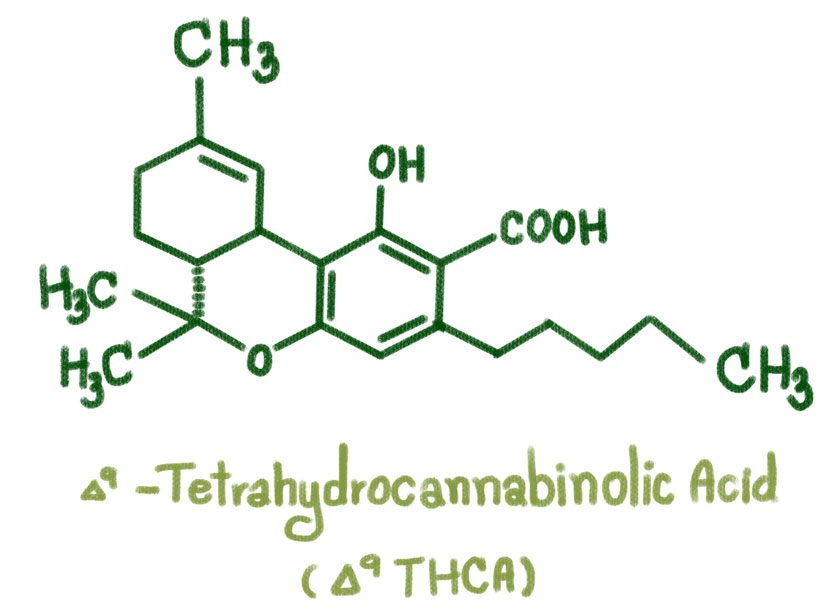
How does THCA become THC? The answer is through heat and light — or the process of decarboxylation. Heat removes a group of atoms from THCA called carboxilic acid, altering the THC chemical structure, thus becoming the perfect shape to fit into our endocannabinoid system (ECS) CB1 receptors and producing the elevated experience.
THCA is believed to have an assortment of medicinal properties. There isn’t a lot of evidence to definitively support this claims so more research needs to be done. Here are some of its properties:
- Anti-inflammatory properties for treatment of inflammatory conditions like lupus and arthritis
- Neuroprotective properties for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
- Anti-emetic properties for treatment of lack of appetite and nausea
- Anti-proliferative properties noted in studies of prostate cancer
Decarboxylation Process
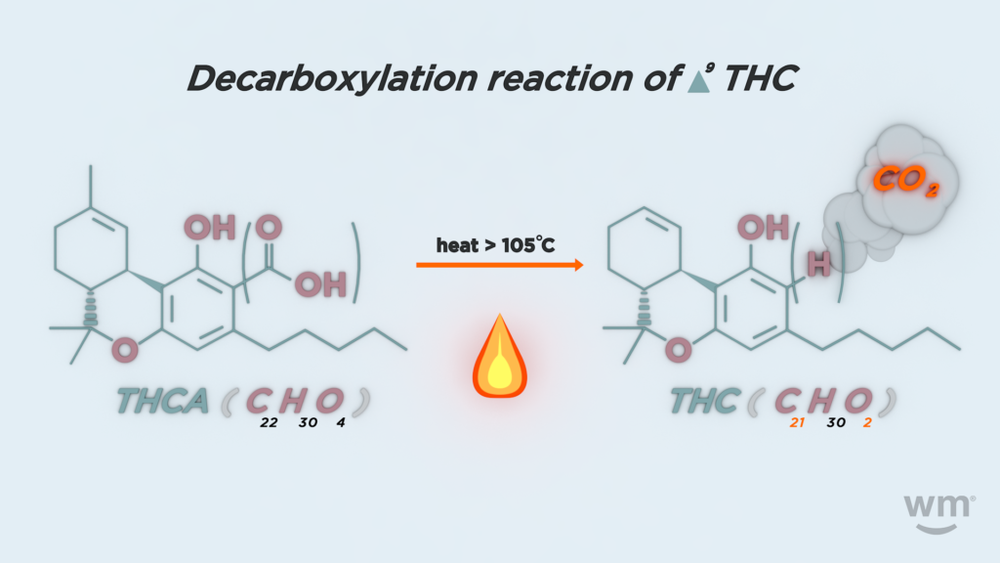
The acidic precursors are considered “thermally unstable,” so they will alter their form when exposed to heat. Because of this instability, the molecules lend themselves to several different methods of decarboxylation.
Here are some ways that weed is decarboxylated:
Sunlight conversion: Over a period of time THCA converts to THC through exposure to heat or light. So eating or juicing raw buds that have been exposed to the sun for a long time might cause unwanted high in some patients.
Smoking: The hot temperature from the combustion process of burning the dry weed will rapidly convert THCa to THC.
Vaporizing: Similarly to smoking it, the heat of the vaporizer unit will convert THCa to THC in a very efficient way.
Cannabis concentrates: THCa can be extracted, isolated and made into crystals that can be consumed in dabs. When heated up THCa will convert to THC.
Conventional oven: Raw Cannabis needs to be activated before making edibles. Usually material gets ground up, spread evenly across a baking sheet, and baked around 230 degrees Fahrenheit, or 110 degrees Celsius, for 30-90 minutes. This will decarboxylate the Cannabis and activate it.

In Conclusion
Understanding the plant’s properties and how and why they interact with our bodies the way they do is extremely important in achieving the maximal benefits while avoiding adverse side effects. Cannabis molecules each have their own benefits and as raw cannabis is further studied, we will learn more about their benefits.
Related
-
Treating Anxiety with Cannabis
A number of distinct compounds play a role in the…
-
Juicing Cannabis: Relief Without The High
The act of juicing leafy greens like kale and spinach…
-
Coronavirus and Medical Cannabis patients in Florida
The OMMU and FL DOH has allowed doctors to do…



