The endocannabinoid system plays many important roles in the human body utilizing its receptors distributed mostly in the brain and gut. It help regulates and keep the body in homeostasis which is the perfect body balance. First discovered while trying to understand the effects of cannabis, and named the endocannabinoid system for this reason.
Because of its widespread effects and therapeutic potential the endocannabinoid system is a major target of medical research. While we have been able to figure out the basics of the system, much more remains to be uncovered and now that more research is allowed soon more information will come out.
What are Cannabinoids?
Cannabinoid are the chemical messages used by the endocannabinoid system. Our bodies produce our own cannabinoids called endocannabinoids.
These interact with cannabinoid receptors named CB1 and CB2 to regulate basic functions including mood, memory, appetite, pain, sleep, and many more.
There’s about 80 different cannabinoids found in Marijuana, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), and are considered exogenous cannabinoids. When consumed, they interact with cannabinoid receptors to produce different physical and psychological effects in the body.
What is the Endocannabinoid system?
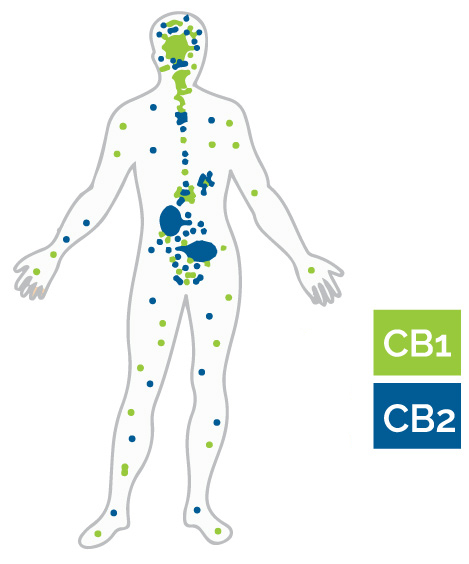
The endocannabinoid system has two receptors known as CB1 and CB2. The distribution of CB1 and CB2 receptors within the brain and body explains why cannabinoids have certain effects
CB1 receptors are distributed throughout the body but, are mostly present in the brain and spinal cord. Found in high numbers in brain regions associated with the behaviors they influence. For example, there are CB1 receptors in the amygdala, which plays a role in memory and emotional processing and the hypothalamus, which is involved with appetite regulation, and . CB1 receptors are also present in nerve endings where they help to reduce sensations of pain.
CB2 receptors tend to be distributed in the peripheral nervous system. They are especially concentrated in immune cells. When these receptors are activated, they help to reduce inflammation which is believed to play a role in many diseases and conditions.
With respect to the cannabinoids found in cannabis, researchers found that THC binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors, activating them just like an endocannabinoid would do.
CBD does not seem to bind directly to cannabinoid receptors. Instead, it works by inhibiting an enzyme called FAAH, which is responsible for the breakdown of Anandamide, the most important endocannabinoid in the body. When FAAH is inhibited, it cannot break down Anandamide at it’s normal rate which leads to a Anandamide buildup in the brain.
How does the ECS work?
Endocannabinoids are cannabinoids produced naturally within the human body and are “short-order” neurotransmitters, meaning they are synthesized on demand. In other words, they are only produced when the body signals that they are needed, and they are only present for a short amount of time.
After released, endocannabinoids are quickly broken down by enzymes, which include FAAH (fatty acid amide hydrolase) and MAGL (monoacylglycerol lipase).
When you consume exogenous cannabinoids like Marijuana, large amounts of cannabinoids enter the body and stick around so the endocannabinoid system is activated more strongly and for longer than it would usually be.
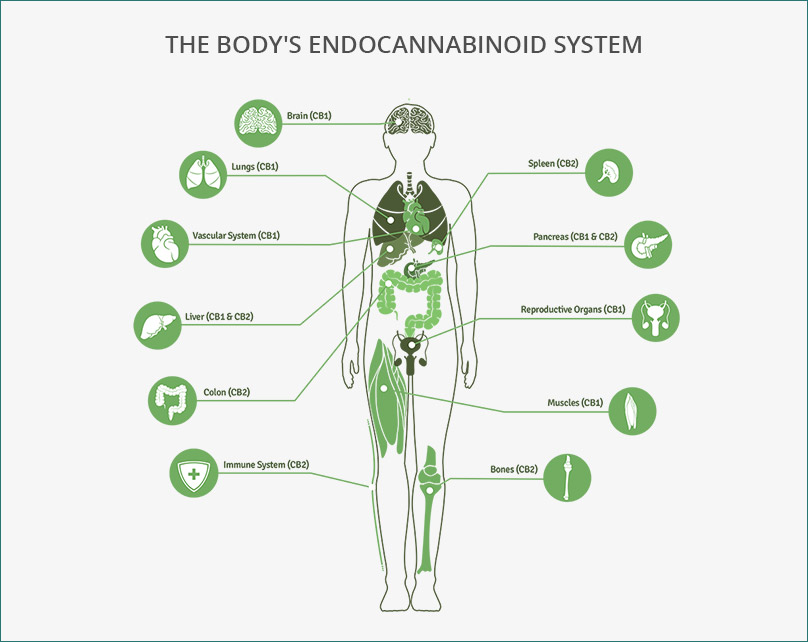
The ECS is involved with regulating many basic functions of the human body, including:
ECS Functions
The ECS is involved with regulating many basic functions of the human body, including:
- Appetite
- Metabolism
- Pain
- Sleep
- Mood
- Movement
- Temperature
- Memory and learning
- Immune function
- Inflammation
- Neural development
- Neuroprotection
- Cardiovascular function
- Digestion
- Reproduction
Besides maintaining basic functions, the ECS also acts in response to illness. Tumor cells,for example, have been shown to express more cannabinoid receptors than healthy cells. Studies also show that patients with conditions like Parkinson’s disease, anxiety, chronic pain and arthritis show higher levels of endocanabinoids.
As a result, some scientists believe the overall function of the endocannabinoid system is to regulate Homeostasis which is a key in maintaining a good balance in life.
Diseases are largely a result of a failure in achieving homeostasis. Thus, the endocannabinoid system’s role in maintaining homeostasis makes it a unique target in medicine.
The Endocannabinoid system and current medicine
Due to its widespread effects in the human body, the endocannabinoid system shows a promising future in treating many diseases and conditions.
There are currently two major ways of targeting the endocannabinoid system: synthetic cannabis and medical marijuana.
Medical marijuana is the most commonly used way of targeting the endocannabinoid system to treat various conditions. Compounds in marijuana, including THC, CBG and CBD, are known to produce therapeutic effects by interacting with the ECS.
Medical marijuana can be used for a wide variety of conditions including chronic pain, nausea, multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, and palliative care.

Despite the success of medical marijuana, some users experience unpleasant side effects, such as feeling dizzy, lightheaded and high. Some people do not enjoy the psychoactive effects of cannabis like paranoia and would prefer a treatment that avoids this.
Some researchers are currently looking into whether the endocannabinoid system can be targeted peripherally using synthetic cannabinoids which cannot cross the blood-brain-barrier. This would avoid the side effects of cannabinoids entering the central nervous system and affecting the brain, in other words feeling high.
In sum, the endocannabinoid system is truly a remarkable treasure for scientists and medical professionals. It is very complex, plays many important roles in many vital processes, and holds promising future as a treatment target for many debilitating conditions.
Related
-
Renewing your MMJ card in Florida
Your MMJ card was given to you by The Florida…